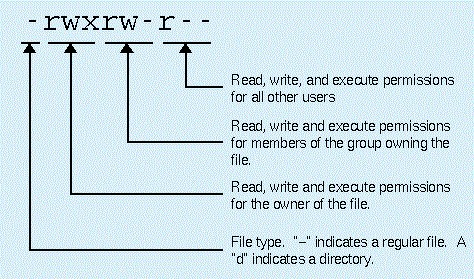
Each file and directory on your system is assigned access rights for the owner of the file, the members of a group of related users, and everybody else. Rights can be assigned to read a file, to write a file, and to execute a file (i.e., run the file as a program).
To see the permission
settings for a file, we can use the ls command as follows:
ls -l
Here we can see:
- The file "vmware-install.pl" is owned by user "root"
- User "root" has the right to read, write and execute this file
- The file is owned by the group "root"
- Members of the group "root" can also read and execute this file
- Everybody else can also read execute this file
Chmod:
The chmod
command is used to change the permissions of a file or directory. To use it, you specify the
desired permission settings and the file or files that you
wish to modify
There are
two ways to use this command:
1.
Absolute
mode
2.
Symbolic
mode
Absolute (Numeric) Mode:
In this
mode file permissions are not represented as characters
but a three digit octal number
The
table below gives numbers for all for permissions types:
Value
|
Binary
|
String
|
Description
|
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
0
1
10
11
100
101
110
111
|
---
- -x
-w-
-wx
r--
r-x
rw-
rwx
|
No Permission
Execute only
Write only
Write & Execute
Read only
Read & Execute
Read & Write
Read, Write & Execute
|
Let's see the chmod command in action:
In the above given image, we have changed the permissions of the file 'vmware-install.pl’ to '764'
764 absolute code says the
following:
- Owner can read, write and execute
- User group can read and write
- Other can only read
This is how you can change
the permissions on a file by assigning an absolute number
Symbolic Mode
In the symbolic mode you can
modify permissions of a specific owner. It makes use of mathematical symbols to
modify the file permissions
Operator
|
Description
|
+
|
Adds a permission to a file or
directory
|
-
|
Removes the permission
|
=
|
Sets the permission and overrides
the permissions set earlier
|
The various owners are
represented as :
User Denotation
|
|
u
|
User/Owner
|
g
|
Group
|
o
|
Other
|
a
|
All
|
We will be using permissions in characters
like rwx:
In the above given image, we are removing write permission for user, read & write permission for group and write permission for others
Chmod u+w,g+rx,o+x (permission) vmware-install.pl (filename)
In the above image, we are adding write permission for user, read & execute permission for group and execute permission for other
Changing file ownership
ls -l
Chown user1 (username) vmware-install.pl (filename)
Changing group ownership:
The group ownership of a file or directory may be changed with chgrp. This command is used like this:
chgrp user (group name) vmware-install.pl (filename)
In the above image, we can see the file vmware-install.pl is now belongs to group user
Changing group and user ownership together:
Chown user1:user (username:groupname) vmwareinstall.pl (filename)
File Permission in Linux
 Reviewed by vijay pratap singh
on
March 26, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by vijay pratap singh
on
March 26, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by vijay pratap singh
on
March 26, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by vijay pratap singh
on
March 26, 2017
Rating:















No comments: